Beating the enemy at its own game
Monday, October 10, 2016
The hosts file plays an important role when criminals are peddling us the website pages they need. By manipulating it, they can hide access to anti-virus vendor websites.
What is the hosts file for? Itâs a file in which you can place records that match the names of Internet resources with their network addresses. For instance, this lets you access various websites without using external services and accelerate website loading speed.
The proactive protection technologies used in Dr.Web Security Space let you control any changes made to the contents of the hosts file.
But the hosts file is a double-edged sword, and in the hands of an experienced user it can prevent fraudulent websites from being accessed. Add the string "127.0.0.1 URL_of blocked_website" to the end of the file to block access to an unwanted website. The point of doing this is that when a user attempts to load a blocked resource, the system will try to load it from the local computer (the predefined address is 127.0.0.1) on which it is obviously missing. Thus, unwanted websites wonât load.
But a hosts file can be modified to do more than combat unwanted resources. As everyone knows, todayâs malicious files are often managed externally.
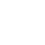
To determine a user's IP address, Black Shades requests http://icanhazip.com. This Black Shades feature gives users a simple way to combat it. Just open the hosts file and add the line 127.0.0.1 www.icanhazip.com. If malware fails to connect to icanhazip.com, it terminates abnormally and displays an error message (shown in the illustration below).
Hosts is a simple text file where one line corresponds to one record. The typical record format is:
IP address Domain_symbol_name # There may be a comment here
In almost all operating systems (except Windows 7 and 8, where there are comments only), the first entry is:
127.0.0.1 localhost
This means that the localhost domain name matches the 127.0.0.1 IP addressâthe systemâs local address.
Important! By default, for Windows it is located in %windir%\system32\drivers\etc\hosts. Criminals can change this path. However, you can reset it to default. For simplicityâs sake, in this example we are assuming that the file path matches the default value.
You can open the file by clicking Start-Run (the same window displays the key combination Win+R); in the newly appeared window Run the program, enter notepad %SystemRoot%\system32\drivers\etc\hosts in the field Open, and click ÐÐ. You can also open the file in any text editor.
If you open the file manually, please note that it can be given the attribute "Hidden". To display such files, you must enable Show hidden files and folders in Folder Options).
Important! Often criminals use blank lines to insert records outside the visible Notepad window. After opening the file, always check whether there is a scroll bar and scroll the window completely.
Rules for editing the hosts file
- Each element must be placed on a separate line.
- The IP address must start at the beginning of the line, and be followed by (on the same line) the corresponding host name.
- The IP address and host name must be separated by at least one space.
- Comments must be preceded by the # sign.
If comments are used in the lines of matching domain names, they must follow the host name and be separated from it by a # sign.
If you are unable to save the file, log in as administrator or run Notepad as Administrator and edit the file.
There are several ways to do this.
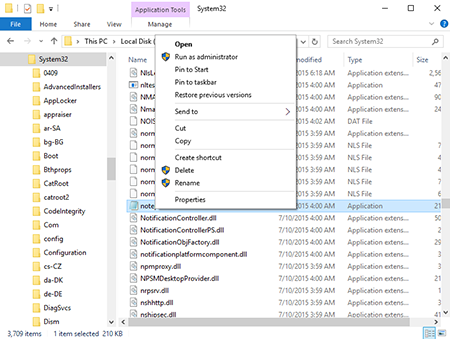
Using the command line (if the system operates under Windows 10) by right-clicking on the icon
 .
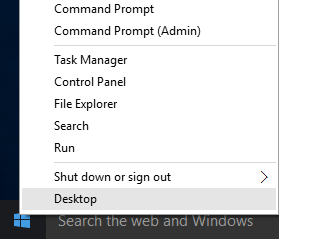
.Select Command Line (Administrator) and in the newly appeared window, write (or copy):
notepad C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts
In this case, an ordinary Windows Notepad will be run as an Administrator and will let you make changes to the hosts file.
Make changes, and save the file (File → Save).
Manually opening a text editor as administrator.
Open the folder that stores an executable text editor like "Notepad" (these instructions will work for other text editors like Notepad++). For instance, the "Notepad" executable file is in C:\Windows\system32. Search for the file notepad.exe (if you use Notepad).
Right-click on the file, and select Run as Administrator.
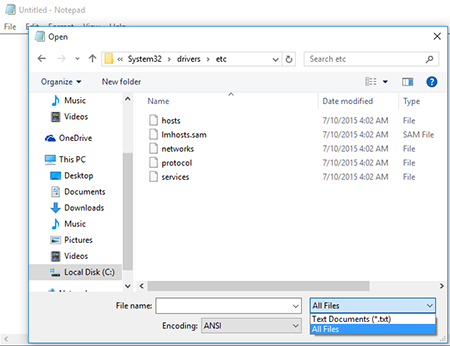
Select File → Open. In the newly appeared window, find the folder C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc. In the lower-right corner, select All files and open hosts.
Make the necessary changes and save the file.
Important! If, after youâve saved the file, and/or after a reboot, some websites are still not opening or are opening and showing unexpected content, the system might be infected with an active malicious program that is checking the hosts file at scheduled intervals and changing its contents.
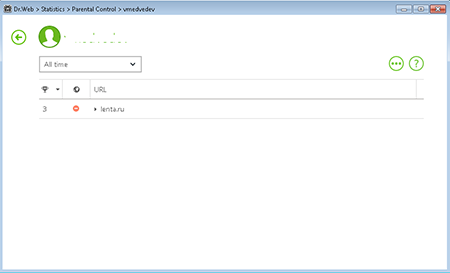
To view statistics on the requests made to different resources and to select those that can be recorded in the hosts file, click on the icon  in the Dr.Web Agent's menu, and select a user name.
in the Dr.Web Agent's menu, and select a user name.
The Anti-virus Times recommends
But there is an easier way!
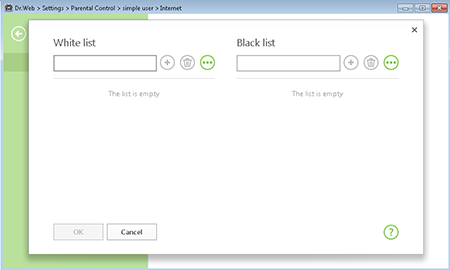
If you want to block access to certain Internet resources, use the whitelists and blacklists of the Parental Control component included in Dr.Web Security Space—if you do, you can configure access rules individually for specific computer users.

![Shared 15 times [Twitter]](http://st.drweb.com/static/new-www/social/no_radius/twitter.png)
Tell us what you think
To leave a comment, you need to log in under your Doctor Web site account. If you don't have an account yet, you can create one.
Comments
vasvet
08:27:27 2018-07-01